Introduction to Bamboo Textiles
Bamboo textiles are quickly becoming a cornerstone of the sustainable fashion movement. Derived from the fast-growing bamboo plant, this eco-friendly fabric is praised for its softness, durability, and minimal environmental footprint.
As the demand for sustainable fabrics rises, bamboo fabric manufacturers are expanding globally to meet market needs. Bamboo is considered a sustainable resource due to its rapid growth and low need for chemicals, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional textile crops. Bamboo is now used in a wide variety of products — from eco-friendly clothing and underwear to luxury bedding and towels.
Benefits of Bamboo Fabric
Why are bamboo textiles gaining popularity worldwide? Because bamboo fabric offers unique benefits:
- Soft and breathable – often compared to cashmere or silk
- Naturally antibacterial – helps reduce odor and bacteria buildup
- Moisture-wicking – perfect for activewear and hot climates
- Hypoallergenic – suitable for sensitive skin
- UV-resistant – offers natural sun protection
Absorbs carbon dioxide and reduces greenhouse gases – bamboo cultivation helps sequester carbon dioxide at a higher rate than many trees, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Prevents soil erosion – bamboo's extensive root system stabilizes soil and helps prevent soil erosion, making it beneficial for the environment.
Additionally, bamboo requires no pesticides and far less water than cotton, making it an eco-conscious choice from crop to closet.
Types of Bamboo Textiles
There are several main types of bamboo textiles used in the fashion and home industries:
- Bamboo Viscose / Rayon: The most common, produced through chemical processing of bamboo pulp. The viscose rayon process involves chemically treating bamboo cellulose extracted from wood pulp to create semi-synthetic fibers.
- Bamboo Lyocell: Created using a closed-loop system with non-toxic solvents. This manufacturing process uses a closed-loop system to extract bamboo fibre in an eco-friendly way, minimizing environmental impact.
- Bamboo Linen: Made using mechanical processes, preserving natural fiber integrity. Natural enzymes are used to break down the bamboo, preserving the strength and quality of the bamboo fibre.
- Blended Fabrics: Bamboo often blended with cotton or spandex for added stretch and durability
Each type offers varying textures, price points, and environmental impacts.
Bamboo fabrics can be woven into a variety of textures and styles, making them versatile for different applications.
Global Market Overview
The global bamboo textile market is expanding rapidly due to growing demand for sustainable alternatives. Bamboo production has increased globally to meet the rising demand for sustainable textiles. Key drivers include:
- Eco-conscious consumers
- Green fashion initiatives
- Versatility of bamboo fibers
- Government incentives for sustainable agriculture
According to market projections, the bamboo textiles industry is expected to grow steadily through 2030 and beyond, particularly in Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America. A significant amount of bamboo fabric is produced in countries like China, India, and Vietnam, contributing to the global market.
Production Process of Bamboo Textiles
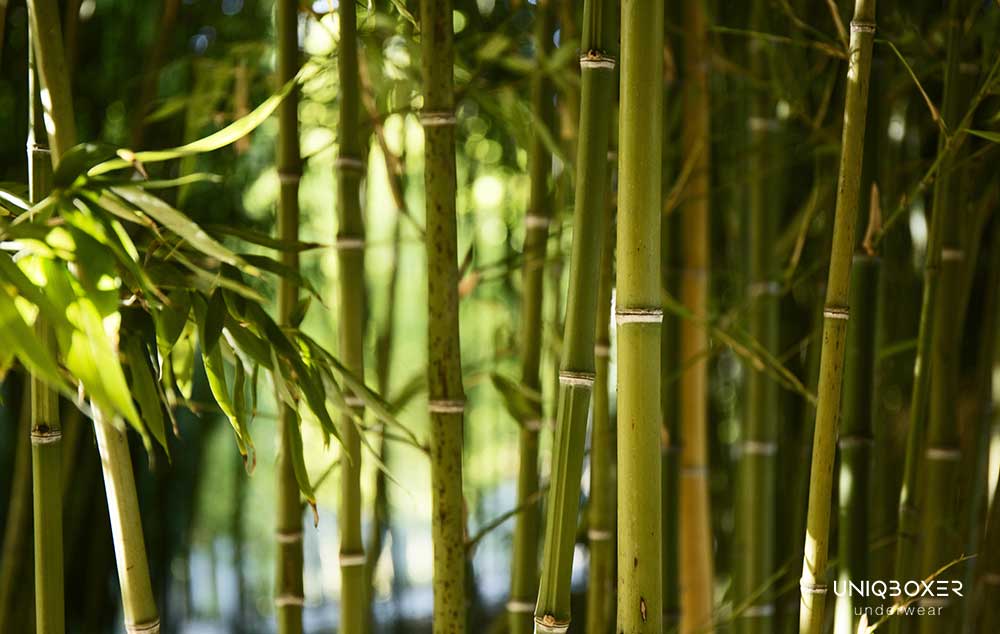
The journey from bamboo plant to finished textile is a fascinating blend of nature and innovation. The production of bamboo textiles begins with harvesting mature bamboo, typically after 3-5 years of growth. Once harvested, the bamboo is cut into smaller pieces and processed into bamboo pulp, which serves as the foundation for creating bamboo fiber.
There are two primary methods for producing bamboo fiber:
- Mechanical Process (Bamboo Linen):In this eco-friendly method, bamboo is crushed and then treated with natural enzymes to break down the bamboo pulp and separate the fibers. The result is a soft, durable, and high quality bamboo fabric known as bamboo linen, or sometimes called bamboo linen. This process preserves the natural integrity of the bamboo fiber, making it a popular choice for those seeking sustainable and environmentally friendly bamboo textiles.
- Chemical Process (Bamboo Viscose/Rayon):The chemical process involves dissolving bamboo pulp using toxic chemicals such as carbon disulfide. This breaks down the cellulose and produces a semi-synthetic fiber known as bamboo viscose or bamboo rayon. While this method allows for mass production of soft and versatile bamboo fabrics, it can have a significant environmental impact if not managed responsibly.
Both methods produce fabrics that are soft and comfortable, but the mechanical process is favored for its minimal environmental footprint and the production of high quality bamboo fabric. As the textile industry evolves, there is a growing emphasis on sustainable production methods that reduce the use of toxic chemicals and promote the use of natural enzymes and closed-loop systems.
Which Countries Produce Bamboo for Textiles?
1. China
– World Leader in Bamboo Fabric
China is the largest producer of bamboo textiles, thanks to its:
- Massive bamboo plantations, with bamboo being an integral part of Chinese culture and industry for centuries
- Mature manufacturing infrastructure
- Key players like Shanghai Tenbro Bamboo Textile Co.
Most of the world’s bamboo viscose and rayon comes from Chinese factories.
2. India
– Growing Investment in Bamboo Farming
India is another major bamboo producer, with increasing investments in:
- Bamboo plantations (especially in Northeast India)
- Textile R&D for bamboo fabrics
- Government support through the National Bamboo Mission
- Utilization of bamboo poles for both traditional crafts and as a raw material in textile production
India is poised to become a global leader in bamboo cultivation and processing.
3. Vietnam
– Emerging Bamboo Hub
Vietnam has become a rising star in bamboo textile production, due to:
- Ideal climate for bamboo cultivation
- Affordable labor and export capabilities
- Strategic trade relations with Europe and the U.S.
- Some Vietnamese manufacturers are exploring the use of bamboo leaves in fiber extraction to enhance sustainability.
Vietnamese manufacturers are gaining global recognition for eco-conscious textile production.
4. Indonesia
– Regional Bamboo Innovation
Indonesia has large bamboo resources and is working to:
- Develop sustainable bamboo supply chains
- Expand into bamboo home textiles and garments
- Increase certifications for export compliance
- Explore the use of bamboo wood as a sustainable raw material for textile production
The country shows strong potential for scaling up eco-textile production.
5. Latin America & Africa
– Untapped Potential
Countries like Colombia, Ecuador, Kenya, and Ghana are beginning to:
- Explore bamboo as an economic crop
- Attract international investors
- Support local textile startups using bamboo fabric
These regions may play a key role in the future diversification of bamboo sourcing.
Bamboo Fabric Manufacturers Around the World
Some of the leading bamboo textile manufacturers include:
- Shanghai Tenbro Bamboo Textile Co., Ltd. (China)
- Bambro Textile Co. (China)
- Boody Eco Wear (Australia)
- Thought Clothing (UK)
- Cariloha (USA)
These manufacturers offer everything from bamboo basics to luxury eco-collections, many using closed-loop or OEKO-TEX certified processes.
Key Players and Industry Trends
The global bamboo textile industry is experiencing rapid growth, driven by rising demand for eco friendly clothing and sustainable textile products. Leading the way is Shanghai Tenbro Bamboo Textile, a pioneer among bamboo fabric manufacturers, renowned for producing high quality bamboo fabric using a closed loop production process that minimizes environmental impact.
Other notable players in the global market include ProECO, W.ELL Fabric, and Mayer Örme Tekstil. These companies offer a diverse range of bamboo fabrics, from bamboo cotton blends to bamboo viscose, catering to the needs of both fashion and home textile industries. The textile industry is increasingly recognizing the unique benefits of bamboo fiber, such as uv protection, moisture wicking properties, and exceptional durability, making bamboo fabrics a preferred choice for eco conscious consumers.
However, the production of bamboo viscose can involve the use of toxic chemicals like carbon disulfide, which raises concerns about the environmental footprint of some bamboo textiles. In response, the vast majority of bamboo fabric manufacturers are shifting towards more environmentally friendly practices, such as adopting closed loop production processes and using natural enzymes instead of harmful chemicals. This trend is helping to ensure that bamboo fabric remains a sustainable and durable alternative to traditional materials like cotton.
As the global market for bamboo textiles continues to expand, the industry is set to see further innovation in production methods, greater transparency, and a stronger commitment to reducing environmental impact. The future of bamboo fabrics lies in balancing high quality production with eco friendly and sustainable practices, meeting the needs of both consumers and the planet.
Environmental Impact of Bamboo Textiles
Bamboo fabrics are widely considered more sustainable than cotton or polyester, but there are caveats. While bamboo textiles are praised for their sustainability, organic cotton is another environmentally friendly fabric option, especially when certified by standards like GOTS for eco-friendly production and minimal environmental impact:
- Bamboo grows quickly and requires less water
- No fertilizers or pesticides are needed
- The chemical process used for viscose can be polluting if not controlled
- Mechanical and closed-loop methods are more environmentally friendly; bamboo lyocell, in particular, is considered a sustainable option due to its eco-friendly processing
- Brands using certified processes (e.g. FSC, OEKO-TEX, or GOTS) offer greater transparency and eco-assurance.
Certifications & Sustainability Standards
To help consumers identify responsible bamboo textiles, several certifications exist:
- OEKO-TEX® Standard 100 – ensures fabrics are free of harmful substances
- FSC® (Forest Stewardship Council) – certifies sustainable bamboo harvesting
- GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) – for blends with organic fibers
- ISO 14001 – for environmental management systems in production
These labels give buyers confidence in the eco-credentials of their bamboo garments.
Applications of Bamboo Textiles
Bamboo fibers are incredibly versatile and used in:
- Clothing and apparel: underwear, t-shirts, loungewear, athletic wear
- Home textiles: sheets, towels, pillowcases
- Medical products: bandages, antibacterial fabric, hospital gowns
- Industrial textiles: eco-friendly packaging, non-wovens
New innovations in bamboo yarn, charcoal-infused fibers, and performance textiles are continually expanding its uses.
Challenges & Opportunities
Challenges:
- High initial cost of sustainable production
- Environmental impact of viscose process if not controlled
- Limited local processing facilities in some countries
- Consumer confusion between “bamboo” and “greenwashed” products
Opportunities:
- Expanding bamboo plantations in Latin America and Africa
- Growth of eco-fashion brands seeking sustainable textiles
- Advances in mechanical and closed-loop bamboo processing
- Increasing consumer demand for transparency and ethics
The future of bamboo textiles lies in innovation, traceability, and sustainability.
Conclusion: A Growing Global Industry
Bamboo is no longer a niche trend — it’s a global textile revolution. From China and India to Vietnam and beyond, the world is embracing bamboo as a sustainable raw material for clothing, bedding, and more.
As the industry evolves, expect more eco-conscious innovations, responsible production practices, and new players in the global bamboo supply chain. For consumers, bamboo textiles offer a way to wear comfort and sustainability — one thread at a time.









Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.